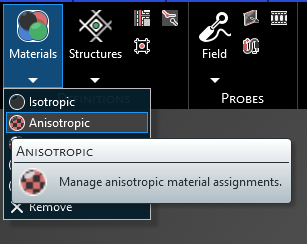
Anisotropic |
Anisotropic materials, in EMA3D, are linear and frequency independent. Anisotropic materials include both electric and magnetic lossy materials characterized by user-supplied entry values in the matrices of the conductivity, the permittivity, the permeability, and the magnetic conductivity tensors. The skin depth arguments, presented in the discussion of isotropic materials above, also need consideration for anisotropic materials, in a similar, although more complex manner. If anisotropic materials overlap, then the last one defined, meaning the last in the EMA3D input file, takes precedence. The region of overlap will, therefore, be redefined to possess the electromagnetic parameters of this last anisotropic material in the input file.
Check to make sure all of the relevant structures in the Structure Tree are checked to make them visible.
Click Materials
 within the Definitions section under the EMA3D tab in the ribbon.
within the Definitions section under the EMA3D tab in the ribbon.
Click
 Anisotropic in the drop-down list.
Anisotropic in the drop-down list.
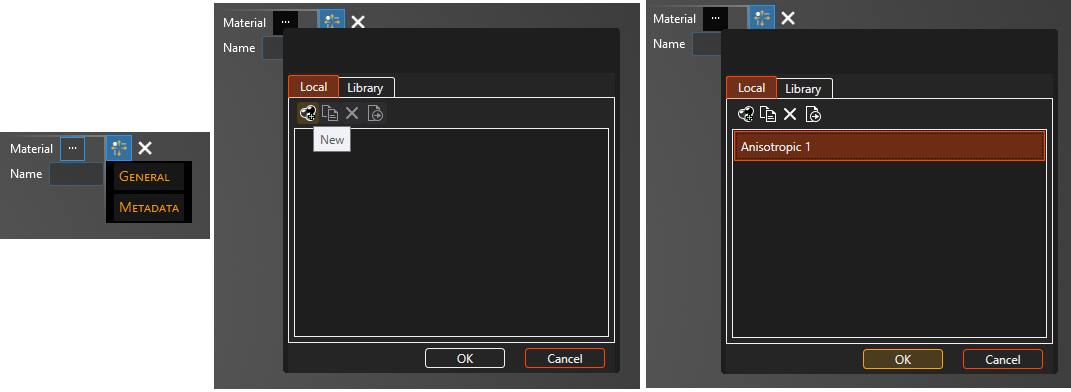
In the Properties panel select the ellipsis to the right of Material. A new window will appear.
In the pop-up window, under the Local tab, select New
 .
.
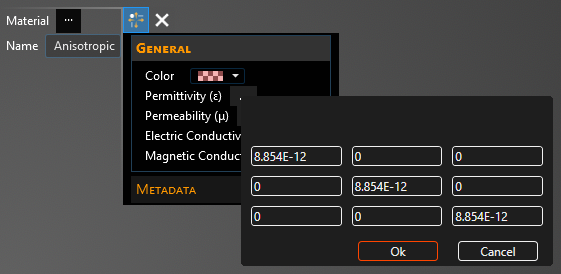
Double click to select the first definition in the list Anisotropic. Click General to view and change any property values. Select a material property to see its definition. A list of material properties and their definitions is provided at the bottom of this page. The color is in A, R, G, B format and choosing an A between 0 (most transparent) and 255 (opaque) can make the color and mesh semi-transparent. The next section discusses how to change the anisotropic material matrix.
Click on the appropriate selection tool (i.e., body
 , surface
, surface
 , or line
, or line 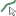 ) tool in the top left of the model window to restrict the assignment definition.
) tool in the top left of the model window to restrict the assignment definition.
To assign material properties, either select the geometric entity in the model window or in the Structure Tree.
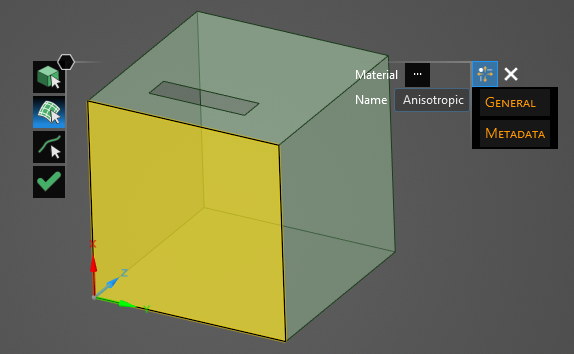
The selected surfaces will be recolored in the model window.
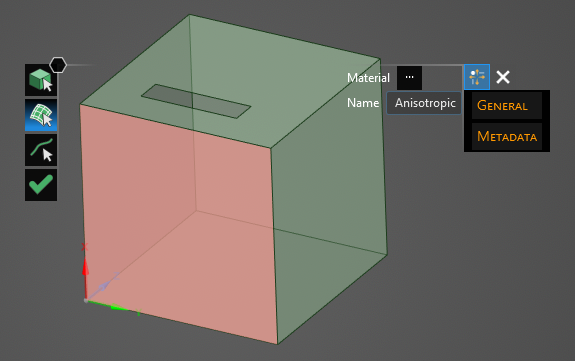
To hide the color and revert to the original, more transparent view, uncheck the check box next to Anisotropic under the Definitions node in the Simulation Tree or uncheck Definitions to hide all materials.
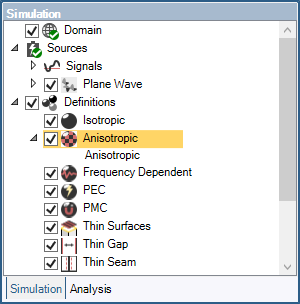
Repeat the above steps to assign as many materials as desired.
Click
 to complete the material assignments.
to complete the material assignments.
Anisotropic material parameters are based on tensor notion as denoted in the matrix below:
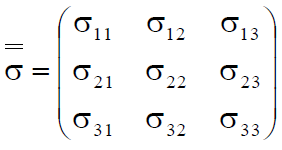
This matrix can be filled out for the various material properties by either selecting the drop-down arrow to the left of the property name (e.g., Permittivity) to reveal the matrix in coordinate form or by selecting the box to the right of the property name then selecting the drop-down arrow, which will reveal the matrix in matrix form.
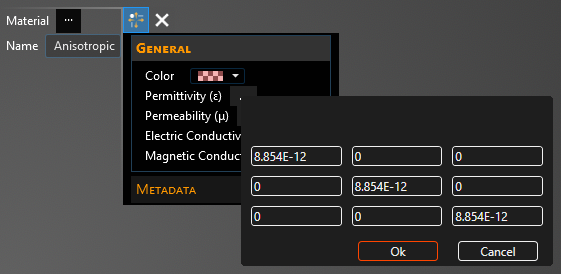
Entry | Meaning |
|---|---|
Name | Display name of the material |
Color | The material display color - format is A, R, G, B and choosing an A less than 255 (opaque) will make the color and mesh semi-transparent |
Permittivity (ε) [F/m] | The material permittivity. The bracketed numbers in the Properties Panel represent the [i,j] tensor notation as in the matrix above. Note: εij ≥ ε0 for i=j and εij ≥ 0 for i≠j. |
Permeability (μ) [H/m] | The material permeability. The bracketed numbers in the Properties Panel represent the [i,j] tensor notation as in the matrix above. Note: μij ≥ μ0 for i=j and μij ≥ 0 for i≠j. |
Electric Conductivity (σe) [S/m] | The material electric conductivity. The bracketed numbers in the Properties Panel represent the [i,j] tensor notation as in the matrix above. Note: σeij ≥ 0 |
Magnetic Conductivity (σm) | The material magnetic conductivity. The bracketed numbers in the Properties Panel represent the [i,j] tensor notation as in the matrix above. Note: σmij ≥ 0 |
Other Resources
EMA3D - © 2025 EMA, Inc. Unauthorized use, distribution, or duplication is prohibited.