EDB Import |
The EDBImport tool lets users use EDB files generated through SIWave or Electronics Desktop. The main features that are imported are the geometry, including dielectrics, vias, traces, and components, which are the RLC passives present in the EDB. The EDBImport automatically assigns materials from the EDB to the geometry and creates point barrier articles to represent the components. This tool allows users to quickly generate a complex model that is ready to mesh and simulate.
Click
 EDBImport under the EMA3D ribbon within the Simulation section.
EDBImport under the EMA3D ribbon within the Simulation section.
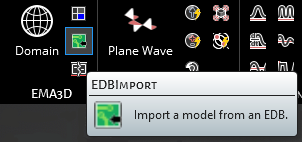
In the heads up display, select the EDB Filepath button. See the first table below for a list of Properties and their meanings.
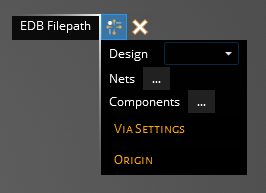
In the pop-up window, navigate to and select the EDB Definition .def file and click Open. Note that the .def file must be in a folder ending with the .aedb extension, which is the default naming convention.
Click
 OK to begin the import. The import process may take several minutes for large, complex files.
OK to begin the import. The import process may take several minutes for large, complex files.
The Simulation Tree will update with the EDB model geometry components, materials, and any definitions that were assigned.
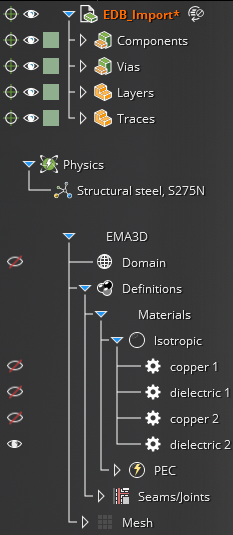
The model geometry and RLC components (red dots, also called barrier articles) will be visible in the model window.
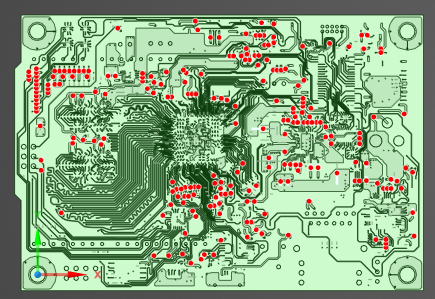
Component values can be viewed and edited by right clicking a red dot in the model window and selecting Edit Barrier Properties.
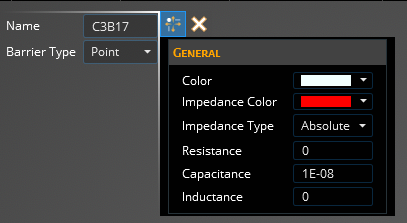
In the heads up display, the name of the RLC component (barrier article) will be visible and the barrier type and other properties can be edited. See the second table below for a list of the properties and their meanings.
Entry | Meaning |
|---|---|
Design | Lists the designs contained in the EDB file. Each design is a separate PCB. |
Nets | Opens editor to choose which nets to import. All nets are imported by default.
|
Components | Opens editor to choose which components to import.
|
Via Settings | Opens menu with options related to via geometry. Tolerance is the distances that traces are receded from a via that is not connected to the trace.
|
Origin | Sets origin for placement of PCB. Origin can also be changed by dragging directional arrows. PCB placement is relative to the origin. For example, a PCB is placed at (5,5) in SIWave. The user sets the origin in EMC Plus to (1,2,3). The PCB would therefore be placed at (6,7,3) when imported. |
Entry | Meaning |
|---|---|
Name | The display name of the barrier article. |
Barrier Type | Whether the barrier article is a single point or a line. |
Color | Display color of the main geometry. |
Impedance Color | Display color of the impedance geometry. |
Impedance Type | Absolute - assigns a given impedance to the barrier article independent of length. Density - assigns an impedance per length to the barrier article. When using the Density specification, the length is associated with the meshed article. In some cases, the meshed length may be longer than the geometric line due to the stair stepping nature of the meshed geometric entities. |
Resistance [Ω or Ω-m depending on the impedance type] | Resistance of the impedance geometry |
Capacitance [F or F-m depending on the impedance type] | Capacitance of the impedance geometry |
Inductance [H or H-m depending on the impedance type] | Inductance of the impedance geometry |
Other Resources
EMA3D - © 2025 EMA, Inc. Unauthorized use, distribution, or duplication is prohibited.