Transmission Line Formalism Equations |
The single conductor transmission line equations are:
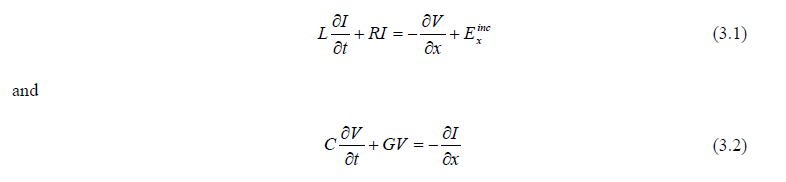
I is the current on the conductor line,
V is the voltage on the line,
C is the capacitance coefficient,
L is the inductance coefficient,
R is the resistance coefficient,
G the conductance coefficient, and
E the external incident electric field along the line.
The external incident electric field (E) is one of many sources of energy that can couple and drive the line. The speed of electromagnetic propagation, v, along the conductor line is defined by:

For a multi-conductor line, the line coefficients, C, L, R, and G, become matrices while I, V, and E become column vectors. The above equations, in matrix form, are:
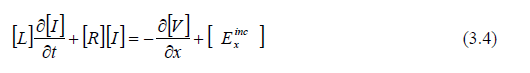
and

Similarly, the speed of propagation is now defined by;

where: [ID] is the identity matrix. The coefficient matrices, or impedance matrices, [C], [L], and [G] are symmetric with off diagonal terms characterizing the coupling between conductors making up the line. The resistance matrix [R] is diagonal.
EMA3D - © 2025 EMA, Inc. Unauthorized use, distribution, or duplication is prohibited.